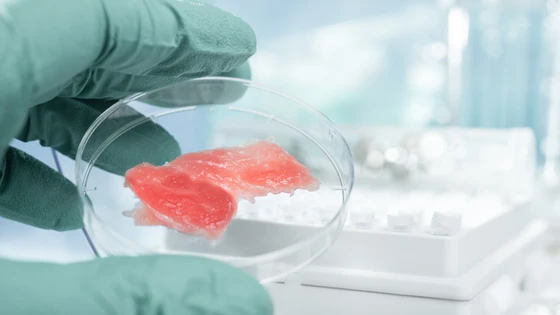
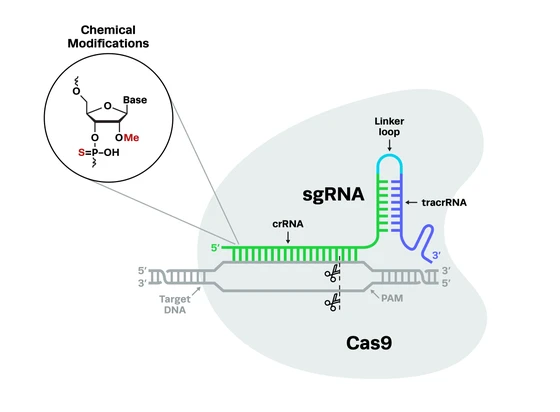
Advancements in biotechnology and gene editing tools like CRISPR are changing the agriculture industry for the better. While CRISPR is being used to produce better crops and sustainable beef, lab cultured meat is another promising alternative.
What does cultured meat mean? Does it taste the same? How is it different from regular meat? We’ll provide you with answers to all of these questions and more. Here’s an overview of what we’ll cover:
- What is Lab-Grown Meat?
- The History of Cultured Meat
- How is Lab Meat Made?
- Challenges of Working with Lab Cultured Meat
- 5 Companies Producing Lab Cultured Meats
- How is Lab Meat Different from Plant-Based Meats?
- How is Lab Grown Meat Different from Conventional Meat?
- Resources to Learn More About Cultured Meats
What is Lab-Grown Meat?
Lab-grown meat, or cultured meat, is produced through the cultivation of animal cells in vitro. Since lab-grown meats are grown from cells, it’s a solution to the ethical issues surrounding livestock agriculture. Cultured meat is produced in a controlled environment, free from bacteria and diseases.
Despite being grown in a lab, lab-grown meat is close to “real” meat, as it is made from animal cells. Although cultured meats are not yet commercially available, research in ongoing on making these marketable in the next few years.
The History of Cultured Meat
Who came up with the idea of cultured meat, and how did it become something that might be hitting grocery store shelves soon? Through years of research and trials, and countless hours of work by numerous scientists, lab-grown meats were created.
Here is a timeline of how and when genetically made meat came about:
|
Year |
Event |
| 1998 | Jon Vein secures a patent for the production of lab-grown meat tissue for the purpose of human consumption. |
| 2001 | NASA begins experiments producing cultured meats with starter cells from turkeys. |
| 2001 | Medical doctor Willem van Eelen, businessman Willem van Kooten, and dermatologist Wiete Westerhof, collectively file a patent for their process of producing cultured meat for consumption. |
| 2002 | The first edible lab-grown meat sample is produced: a fish fillet made from cultured goldfish cells. |
| 2003 | Tissue Culture and Art Project and Harvard Medical School used stem cells from frogs to create tissue that resembled a steak. |
| 2008 | PETA offers one million dollars to the first company that can bring lab-grown chicken to the food industry. |
| 2009 |
Time magazine labels cultured meat one of the breakthrough ideas of the year. |
| 2013 | The first lab-grown beef hamburger was consumed at a press event. The burger was created by Dr. Mark Post at Maastricht University in the Netherlands, and the event was hosted in London, England. |
| 2015 | Maastricht University held their first International Conference on Cultured Meat. |
| 2016 | An engineered meat startup company, Memphis Meats, posts a promo video showcasing their lab-grown meatballs. |
| 2016 | An Isreali company, SuperMeat, runs a crowdfunding campaign to raise money for their efforts to bring lab-grown poultry products to market. |
| 2017 | Finless Foods announces that they expect to bring sustainable, lab-grown seafood to consumer markets within 2 years. |
| 2018 | Dutch startup company Meatable claims they will be able to produce cultured meat from stem cells sourced from animal umbilical cords, solving the problem of needing to kill an animal initially to get starter cells for production. |
How is Lab Meat Made?
Lab grown meat is made by the controlled culture of animal cells. Scientists commonly grow cells in the lab, and this process is not too different. While the specifics behind how lab meat is grown in companies is proprietary, the basics behind it consists of keeping cells happy in a culture environment to promote their survival and continued growth.
Lab grown meat starts with animal cells, typically muscle or fat cells, or stem cells that are forced to differentiate into muscle cells. These cells are cultured using the appropriate growth medium that contains nutrients that promote its growth and survival. To aid in the growth of culture as it begins to expand, edible scaffolding is sometimes used. Finally, cells are allowed to divide and expand until ready to use, all the while being monitored consistently for harmful bacterial contamination.
Challenges of Working with Lab Cultured Meat
In addition to the societal stigma that lab made meat faces, there are other challenges that come along with creating meat products that resemble traditionally-sourced meats, including replicating texture, appearance, and taste. Here are some of the main difficulties:
1. Speed and density of cell growthThis is a challenge because while individual cells can grow quickly, it can take some time for a larger tissue segment to form. In addition, if the cells aren’t forming together at the same density as traditionally sourced meat, the texture of the product won’t come out the same way.
This is a challenge because while individual cells can grow quickly, it can take some time for a larger tissue segment to form. In addition, if the cells aren’t forming together at the same density as traditionally sourced meat, the texture of the product won’t come out the same way.
CRISPR 101 eBook
CRISPR has quickly become a standard laboratory tool for gene editing. As the adoption of CRISPR accelerates worldwide, up-to-date knowledge of the basics of CRISPR is essential for anyone in the field. From target identification studies to the recent breakthroughs in clinical trials, CRISPR is enabling scientists to unlock the power of the genome.
Download our CRISPR 101 eBook today to stay up to date on all your CRISPR basics and get the best results in your CRISPR experiments!

2. Growth medium requirementsCells require proper growth medium rich in nutrients in order to survive and grow. Since lab grown meat is ultimately meant for human consumption, the high quality growth medium free of common allergens are necessary.
Cells require proper growth medium rich in nutrients in order to survive and grow. Since lab grown meat is ultimately meant for human consumption, the high quality growth medium free of common allergens are necessary.
3. Lack of blood vesselsBlood vessels normally deliver blood to tissue to survive. In lab-grown tissues, blood vessels are not present, so scientists must think of new ways to deliver nutrients, taking the place of naturally occurring blood vessels.
Blood vessels normally deliver blood to tissue to survive. In lab-grown tissues, blood vessels are not present, so scientists must think of new ways to deliver nutrients, taking the place of naturally occurring blood vessels.
4. Cost to produceLab-grown meats are still only being produced on a fairly small scale, and though the cost to make them has drastically decreased from the $330,000+ it used to cost, lab meat is very expensive to produce at around $2400/pound of lab beef, according to Memphis Meats. If adopted by larger companies and produced on a large scale, the cost will be reduced significantly.
Lab-grown meats are still only being produced on a fairly small scale, and though the cost to make them has drastically decreased from the $330,000+ it used to cost, lab meat is very expensive to produce at around $2400/pound of lab beef, according to Memphis Meats. If adopted by larger companies and produced on a large scale, the cost will be reduced significantly.
5. Replicating the taste of traditional meatTo motivate meat lovers to switch to lab-grown meat, the taste needs to be the same or very close to that of traditional meat. Many people would be quite put off if the taste leaves too much to be desired. More work is needed to ensure that the taste of cultured meat will please the foodies of the world.
To learn more, check out this article on the main difficulties of working with cultured meats.
To motivate meat lovers to switch to lab-grown meat, the taste needs to be the same or very close to that of traditional meat. Many people would be quite put off if the taste leaves too much to be desired. More work is needed to ensure that the taste of cultured meat will please the foodies of the world.
To learn more, check out this article on the main difficulties of working with cultured meats.
5 Companies Producing Lab Cultured Meats
There are now several companies working on bringing lab-grown meat and seafood products to consumer markets worldwide. Here’s a rundown of five awesome companies creating these products:
1. Memphis Meats

Memphis Meats had the idea for cell-based meats and poultry products in 2005, and in 2015, they finally launched and began producing the meats. They created the world’s first cell-based meatball in 2016, with poultry following shortly after in 2017.
Under the vision and execution of CEO & founder Dr. Uma Valeti, Memphis Meats hopes to scale in such a way that less land, water, energy, and food inputs are consumed by the meat industry, and quality, healthy, and safe cell-based meats can reach grocery stores in coming years.
2. Finless Foods

As their slogan states, Finless Foods offers you “sustainable seafood, without the catch.” They are bringing sustainable, cell-based seafood products to your table, starting with bluefin tuna. This achievement would help solve the environmental problem that commercial fishing is causing, and would improve the nutritional quality of the fish being consumed.
3. Meatable

Meatable is creating hamburgers from single animal cells, in a much faster, cleaner, and more sustainable way than traditional livestock-sourced burgers. Their process claims to produce a hamburger in 3 weeks or less, which, when compared to the minimum 3 years traditional meat takes, is a significant improvement. You can check out their product creation cycle to learn more about the timeline of this process.
4. SuperMeat

SuperMeat got started through a crowdfunding campaign on Indiegogo. They’re working to create animal-friendly meat products in partnership with PHW-Gruppe, one of Europe’s largest poultry producers.
Like all the other companies here, their product will help solve the environmental impact issues of the meat industry, but SuperMeat’s marketing and branding also focuses on the humanity of how this type of meat production will prevent the slaughter of animals.
5. Mosa Meat

Mosa Meat was the groundbreaking company responsible for the first lab-grown hamburger showcased in 2013. Since then, they’ve been hard at work to get their products ready for commercial production, and are aiming to make them available to consumers within the next few years.
Their main goal is to bring cultured meat (or “clean meat” as they call it) to the mass market to help satisfy the growing demand for meat, which they believe will hit a critical stage by 2050. They also claim that while the process is very expensive now, over time, they will be able to reduce the price to about the same as a typical beef hamburger in the supermarket.
How is Lab Meat Different from Plant-Based Meats?
A new wave of meatless meats are becoming more popular since coming to the market in the last few years, however it is important to distinguish that those are not the same as cultured meat. The meatless meats you might be familiar with are plant-based ‘meats’ and contain no animal tissue whatsoever, though can sometimes contain animal byproducts like eggs.
The ingredients listed in a lab meat hamburger would be “ground beef” while common ingredients in a plant-based burger made famous by companies like Impossible Foods or Beyond Meat include soy, beans, tofu, vegetables, grains, mushrooms, and other non-meat products.
Cultured meat is not synonymous with vegetarian or vegan-safe foods, as it contains animal cells. While lab cultured meats are not vegetarian, they provide a more friendly alternative for those who choose to refrain from eating meat because of animal cruelty or environmental reasons.
How is Lab Grown Meat Different from Conventional Meat?
If lab produced meats are similar in appearance, texture, and taste to conventional meat, how are they different? Are the products the same? Is there a reason to choose one over the other?
Here are the ways cultured meat differs from traditionally-sourced meat:
|
Lab Meat |
Conventional Meat | |
| Artificiality | Grown from animal cells in vitro i.e. in controlled lab conditions | Comes directly from animals that have been sacrificed for consumption |
| Impact on environment | More environmentally friendly due to lack of greenhouse gas production | High environmental impact with land occupancy and greenhouse gas emissions |
| Ethics | A more ethical alternative as animal cells are used | Killing animals for consumption raises ethical issues |
| Health | Harmful additives are minimized in lab grown meats | May contain additives like growth hormones, antibiotics, and other chemicals |
| Cost to produce | Due to its process, lab grown meat is currently very expensive to produce | Traditional meat is fairly affordable for an average person to buy |
Resources to Learn More About Cultured Meats
Looking to learn more about genetically modified meat, how it is made, and when you might get to use it in your favorite home-cooked meals? Check out these awesome resources for more information on cultured meats:
Lab-Grown Meat - Meat Produced without Killing Animals is Heading to Your Dinner TableScientific American dives into the potential benefits of lab-grown meat, and the barriers the industry will have to overcome in order to become integrated into consumers’ daily lives.
Scientific American dives into the potential benefits of lab-grown meat, and the barriers the industry will have to overcome in order to become integrated into consumers’ daily lives.
Here Are 5 Things You Should Know About Lab-Grown MeatInteresting Engineering details issues with our society’s rate of meat consumption and how cultured meats could help solve them.
Interesting Engineering details issues with our society’s rate of meat consumption and how cultured meats could help solve them.
The Truth About Lab-Grown MeatScienceLine answers some frequently asked questions about lab made meat.
ScienceLine answers some frequently asked questions about lab made meat.
Is the World Ready for Lab-Grown Meat?“Do people want to eat lab grown meat?” The Guardian’s Jacy Reese discusses whether lab meat will be globally accepted.
“Do people want to eat lab grown meat?” The Guardian’s Jacy Reese discusses whether lab meat will be globally accepted.
CRISPR 101 eBook
CRISPR has quickly become a standard laboratory tool for gene editing. As the adoption of CRISPR accelerates worldwide, up-to-date knowledge of the basics of CRISPR is essential for anyone in the field. From target identification studies to the recent breakthroughs in clinical trials, CRISPR is enabling scientists to unlock the power of the genome.
Download our CRISPR 101 eBook today to stay up to date on all your CRISPR basics and get the best results in your CRISPR experiments!